Global Branding: The Complete Guide 2025
Published on January 5, 2025 by Anisha Patel

Global branding is a strategy that helps businesses become a known household name in unknown countries. Imagine walking into a store in another country and seeing a brand you recognize instantly. Well, that’s what global branding can do if done correctly.
It’s about creating a strong, recognizable presence across different markets, ensuring that your brand is perceived similarly to local products no matter where it is sold.
In today’s interconnected world, global branding is more than just a strategy. If you are looking to expand your business beyond local borders, global branding is the answer.
Global branding is not only about selling products but about creating an identity that resonates with people across the globe.
In this detailed guide, we’ll learn what global branding is, why it’s crucial for your businesses and how you can create a successful global brand. I’ll also share a few successful examples.
What is Global Branding?
Global branding is a strategy used to create and manage a consistent brand identity (look, feel, personality and message) across multiple countries and diverse cultures.
Every country has their own culture and market which is different from the world. People speak different languages and have their own tastes and preferences. When you want to sell something to them, you’ll have to adapt to their culture.
Now, imagine you want to expand to multiple countries. Creating and maintaining a completely different brand identity for each country will be impossible to manage. That’s why we make one global brand.
Global branding is about maintaining one consistent brand identity and then adapting it to different cultures without changing the core. The main goal of global branding is to establish a recognizable, credible and trusted presence worldwide.
Whether someone is in New York, Tokyo, or Mumbai, your brand should evoke the same feelings, convey the same message, and stand for the same values no matter where it appears.
Key Elements of Global Branding
Global branding is formed by three key elements: consistency, adaptation and cultural sensitivity.
Consistency: It is about maintaining a uniform identity, message and experience across different markets ensuring that their core values, visuals, and customer experience remain consistent.
Adaptation: It is about changing certain aspects of a global brand such as marketing messages, product offerings, or packages to meet local market needs, preferences, or cultural differences.
Cultural Sensitivity: It is about being mindful of how their products, messaging, or business practices may be perceived across cultures.

Let’s take three examples to understand this:
Example 1: Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola maintains consistent visual branding worldwide, using the same logo, red-and-white color scheme, and packaging style across all markets.
Whether in the U.S., Asia, or Africa, the look and feel of the Coca-Cola brand remains the same, ensuring that consumers recognize it instantly, no matter where they are.
Example 2: McDonald’s
While McDonald’s maintains consistency in its core brand values and restaurant design, it adapts its menu to local tastes.
In India, for example, McDonald’s offers items like the “McAloo Tikki” burger, which caters to the vegetarian preferences of the local market. By adapting its product offerings while keeping its brand identity intact, McDonald’s can successfully appeal to diverse audiences globally.
Example 3: Procter & Gamble (P&G)
When P&G launched its “Thank You, Mom” campaign during the Olympics, it adapted the messaging in various regions to align with cultural values about family and motherhood.
For example, in Japan, where collectivism and respect for elders are emphasized, the campaign focused on the mother’s role in nurturing family harmony. This cultural sensitivity allowed the brand to connect with audiences on a deeper emotional level.
Global Branding Vs. Local Brand
To create a successful global brand it’s important to understand what a local brand is and how is it different from a local brand.
Local brand focuses on a single market whereas global brands focus on multiple markets.
Unlike local branding, where the focus is on a single market, global branding requires a broader approach. Here you have to balance between standardization (keeping the brand consistent)and customization (adapting it to fit local tastes).
| CRITERIA | GLOBAL BRAND | LOCAL BRAND |
|---|---|---|
| Market Reach | Operates in multiple countries worldwide. | Limited to a specific region or country. |
| Brand Recognition | High, due to global exposure. | Recognized primarily within a local area. |
| Target Audience | Diverse and international. | Niche and specific to local demographics. |
| Marketing Strategy | Standardized with slight regional variations. | Tailored to local culture and preferences. |
| Product Consistency | Highly consistent across regions. | May vary significantly by region. |
| Adaptability | Sometimes less adaptable to local needs. | Highly adaptable to local trends and tastes. |
| Cost Structure | Can afford large-scale production and marketing, potentially reducing costs. | Smaller scale, potentially leading to higher unit costs. |
| Customer Loyalty | Moderate, driven by global reputation. | Often higher, driven by local identity and community ties. |
| Cultural Relevance | May struggle with deep cultural integration. | Typically closely aligned with local culture and values. |
| Pricing Strategy | Standardized pricing globally, though it may adjust based on region. | Pricing often reflects local market conditions. |
| Innovation | Can afford high investment in innovation. | Can afford the high investment in innovation. |
| Competition | Faces competition from both global and local brands. | Primarily competes with other local brands. |
| Sustainability | May invest in global sustainability practices. | Focus on local, community-centered sustainability efforts. |
| Customer Engagement | Digital and mass media, with less direct interaction. | Often more direct, personal interaction with customers. |
Now that you understand what a global brand is, what is consists of and how is it different from a local brand, let’s look at 10 benefits of global branding.
10 Benefits of Global Branding
Building a global brand has a lot of benefits. It enhances your business’s trustworthiness and credibility, making people more inclined to like and buy from you. Plus, it gives you a competitive edge and increases your chances of success.
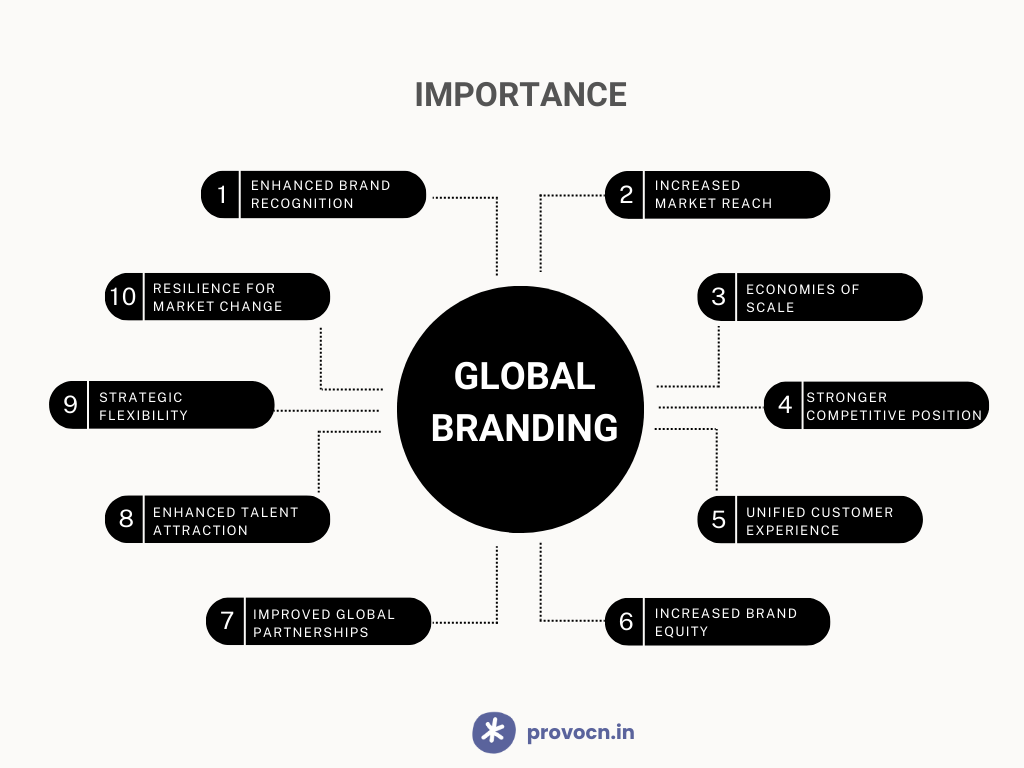
1]. Enhanced Brand Recognition
Global branding helps you create a consistent and recognizable brand image across the globe. For example Coca-Cola: Its iconic red-white logo and contour bottles are recognized by almost everyone, everywhere.
When a brand maintains a unified identity (like Coca-Cola or Apple), it makes it easy for people to identify it. When so many people recognize a brand (for good reasons), they will buy from it.
This increases trust in the brand, positions it in both local and international markets and increases overall sales.
2]. Increased Market Reach
When you build a global brand, you increase your reach to new and diverse markets which allows you to tap into a large customer base, potentially increasing sales and revenue.
When you operate in multiple countries it also reduces risks associated with economic fluctuations in any single region.
3]. Economies of Scale
To efficiently run a global brand you’ll have to standardize the marketing and production processes which can lead to reduced costs and improved efficiency.
Bulk purchasing, streamlined operations, and centralized management contribute to more cost-effective business practices.
4]. Stronger Competitive Position
A well-executed global branding strategy can enhance a company’s competitive position. By establishing a strong and recognizable brand globally, you can differentiate your company from local competitors.
This differentiation helps build brand loyalty and makes it more challenging for new competitors to compete effectively.
5]. Unified Customer Experience
Global branding ensures a consistent customer experience regardless of location. Customers expect the same quality, values, and message from a brand, whether they are in New York or Tokyo.
This consistency helps build trust and loyalty among consumers, leading to increased customer satisfaction and retention.
6]. Increased Brand Equity
A strong global brand contributes to higher brand equity, which can translate into increased brand value. Brand equity refers to the added value a brand brings to a company beyond its tangible assets.
A globally recognized brand often enjoys higher perceived value, allowing for premium pricing and greater market leverage.
7]. Improved Global Partnerships
Companies with strong global brands are more likely to attract international partnerships and collaborations. Businesses seeking to enter new markets or expand their reach often prefer to associate with well-known, reputable brands. These partnerships can lead to new opportunities, joint ventures, and increased market access.
8]. Enhanced Talent Attraction
A global brand can attract top talent from around the world. Skilled professionals are drawn to companies with strong, positive reputations and a global presence.
A well-regarded brand can help in recruiting and retaining employees, contributing to a more talented and motivated workforce.
9]. Strategic Flexibility
Global branding provides companies with greater strategic flexibility. A strong global presence allows businesses to adapt their strategies to changing market conditions, consumer preferences, and economic trends.
This agility helps companies stay relevant and competitive in a dynamic global marketplace.
10]. Resilience to Market Changes
A well-established global brand can offer resilience against market fluctuations and regional downturns. By diversifying across multiple markets, companies can reduce their dependence on any single market.
This geographical diversification helps mitigate risks and ensures a more stable revenue stream, even in challenging economic times.
Let’s look at 10 problems with global branding.
10 Problems with Global Branding
Global branding offers many advantages, but it also comes with several challenges. Here are some of the common problems:
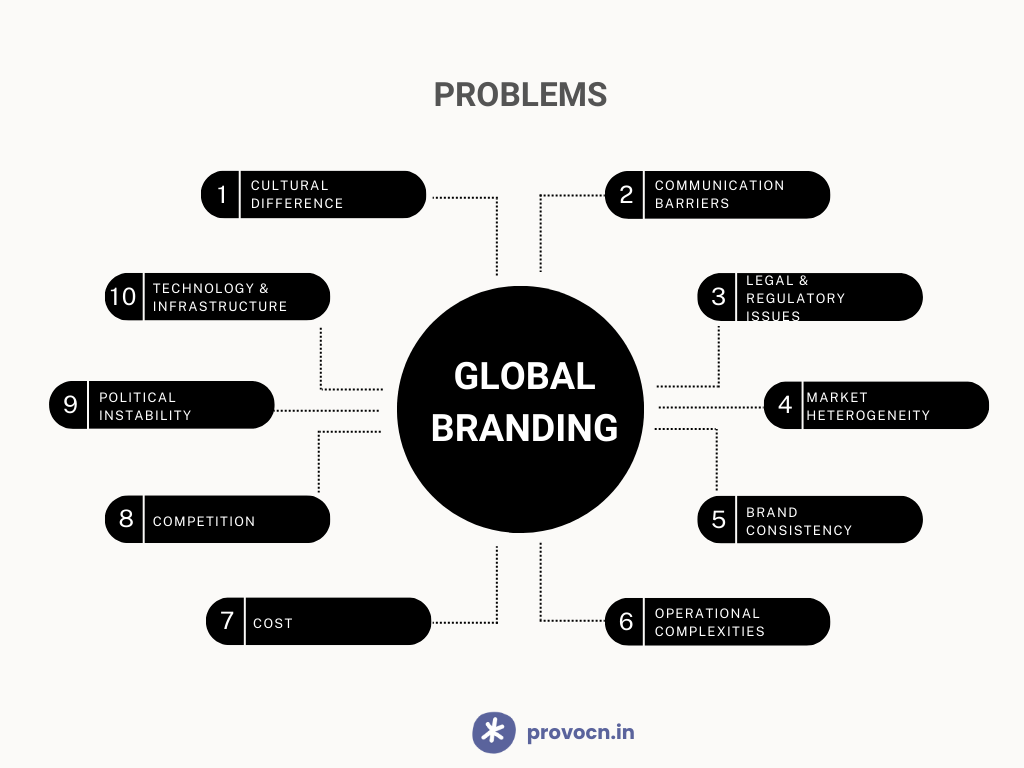
1]. Cultural Differences
To expand your brand globally you need to have a deep understanding of diverse cultural norms, values, and consumer preferences.
Each market has its own unique identity shaped by historical, social, and economic factors which makes it tough to create a brand message that resonates universally.
What might be perceived as an effective marketing strategy in one country could be completely misunderstood or even offensive in another.
2]. Communication Barriers
Language differences present a significant challenge in global branding, as they can easily lead to misinterpretations of brand messages, slogans, or marketing materials.
When expanding into new markets, simply translating content word-for-word often falls short of capturing the intended meaning, tone, and emotional resonance of the original message.
Languages are deeply intertwined with culture, and certain phrases or idioms may not have direct equivalents in other languages, leading to confusion or unintended meanings.
3]. Legal and Regulatory Issues
Navigating the complex web of regulations across different countries is a significant hurdle in global branding. Each country has its own set of laws governing advertising, product labelling, and intellectual property, and these regulations can vary widely.
What is considered a permissible advertisement in one country might be restricted or outright banned in another due to differing standards on content, claims, or target audiences.
4]. Market Heterogeneity
Consumer behaviour and preferences can vary widely across regions, making it difficult to create a one-size-fits-all brand strategy. Brands must balance between standardization and adaptation, which can be resource-intensive.
5]. Brand Consistency
Brand consistency in global branding refers to maintaining a cohesive and unified identity across all markets and platforms, regardless of geographic or cultural differences.
This means ensuring that the brand’s core elements—such as logos, colour schemes, typography, messaging, tone, and overall aesthetic—are the same or aligned across all touchpoints, from advertising to packaging to digital presence.
6]. Operational Complexities
Managing a global brand involves complex coordination across different teams, which can be logistically challenging. Issues like time zone differences, language barriers, and cultural variations can complicate communication.
Supply chain management is also tricky, with varying levels of infrastructure and local regulations affecting product distribution.
Additionally, different market developments require tailored strategies. Effective coordination and communication are essential to overcome these hurdles and maintain a consistent brand presence.
7]. Cost
Global branding requires a significant investment in research, marketing, and localization, which can be costly.
Companies must conduct thorough market research, tailor marketing campaigns, and adapt products to fit local preferences, all of which add to expenses.
8]. Competition
When a global brand enters a new market, it often faces the challenge of competing against established local competitors who understand the market’s dynamics, consumer preferences, and cultural nuances.
These local players have built strong customer loyalty through consistent service and products tailored to local tastes.
This requires balancing their global identity with local adaptation, whether by adjusting marketing messages, products, or even business practices.
9]. Political and Economic Instability
Global branding is highly susceptible to the influence of political and economic changes within individual countries.
Such changes can dramatically affect consumer behaviour, regulatory frameworks, and the overall business environment, presenting significant challenges to maintaining a cohesive global brand strategy.
10]. Technology and Infrastructure
When expanding globally, you also need to take care of varying levels of technological advancements and infrastructure across different countries.
- If a country has access to high-speed internet, widespread smartphone usage and a robust digital ecosystem you can focus more on digital marketing. You can run targeted ads, and social media campaigns and operate on an e-commerce website.
- Whereas in countries with limited internet penetration and slow internet, you’ll have to rely more on traditional marketing. You’ll also have to rethink their digital assets and offer lightweight versions of websites, mobile apps, or advertisements that are optimized for slower connections.
Now that you understand what a global brand is, what makes it different and the pros and cons of it, let’s get to the main topic which is building a global brand.
Build a Global Brand In 7 Steps
Building a global brand is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Here’s how you can create a successful global brand:
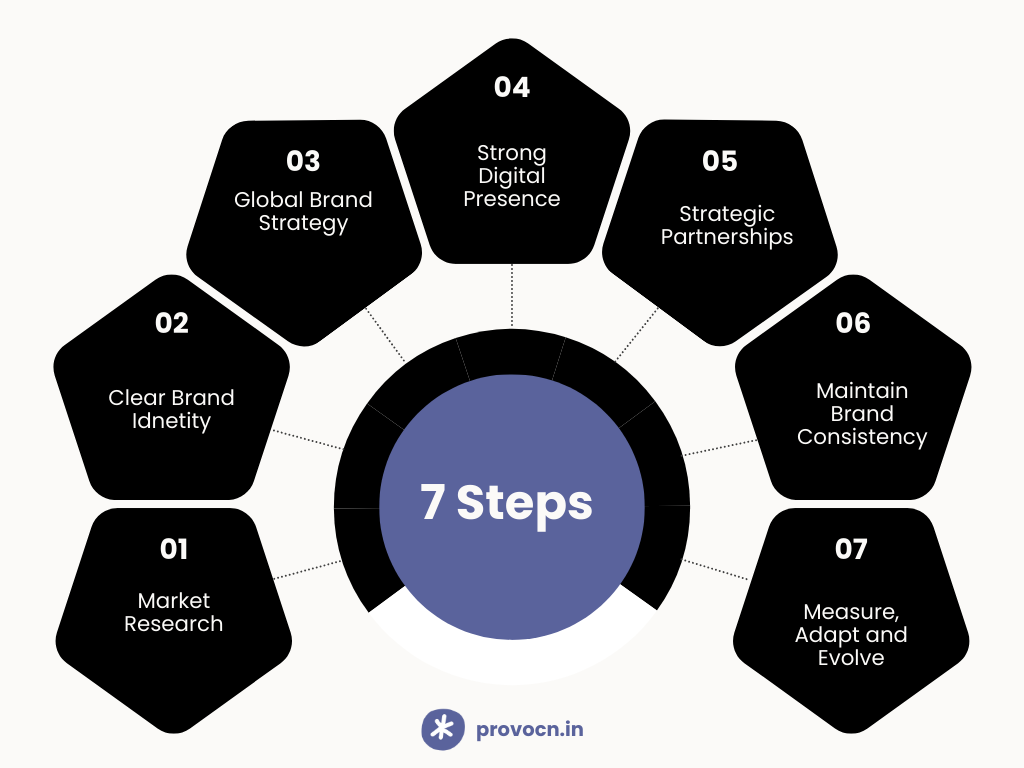
Step 1: Market Research
You are going to enter a new market, so conducting deep market research is crucial. First, understand the cultural norms, values, and consumer behaviours of each region you want to enter and then ensure your brand message truly connects with the local audience.
And don’t forget to keep an eye on local competitors. Studying them and identifying any market gaps will help you find ways to stand out.
Step 2: Clear Brand Identity
Remember the three key elements that we discussed earlier? The first element is consistency. In step 2, we’ll establish the core values that will be consistent across the globe. These values will form the foundation of your brand.
Next, craft a brand message that’s flexible enough to adapt to different cultures but still true to your core identity. This way, your message will resonate universally while maintaining its essence. Try to keep it broad, like Nike’s Just Do It.
And don’t overlook the importance of a recognizable visual identity. Make sure your logo, colour scheme, and overall design are consistent and easy to spot, so your brand feels familiar and trustworthy across all markets.
Step 3: Global Brand Strategy
Now you’ve to figure out whether you’re going to standardize your approach across the board or adapt it for each local market. The most successful brands usually strike a balance between the two.
It’s also crucial to set some clear, measurable goals for your global branding efforts—think along the lines of boosting brand awareness, expanding into new markets, or building customer loyalty. Having these goals will keep you focused and help you track your progress as you go.
Step 4: Strong Digital Presence
Building a strong digital presence is key to global branding. Start by creating localized versions of your website for each market, making sure the content speaks to the local language and culture.
When it comes to social media, use the platforms that are popular in each region to connect with local audiences—just remember to tailor your content to fit the unique preferences of each platform’s users.
And don’t forget about SEO. Optimize your site with local keywords and search behaviours to make sure your brand is easily discoverable wherever you are.
Step 5: Strategic Partnerships
Developing strategic partnerships can really boost your global branding efforts. Start by teaming up with local influencers who have a strong following in your target markets—they can help build credibility and expand your reach.
It’s also a great idea to form alliances with local businesses or distributors to increase your brand’s presence and make it more accessible in new areas.
And don’t forget about global partnerships! Working with international partners can help you scale your brand efficiently across multiple regions, giving you a solid foundation for global success.
Step 6: Maintain Brand Consistency
Maintaining brand consistency is crucial for a strong global presence. Create detailed brand guidelines that cover everything from tone and messaging to visual identity, ensuring that your brand is presented consistently across all markets.
It’s also important to train local teams or partners so they fully understand and follow these guidelines, while still allowing for some necessary local adaptations.
Regularly check your marketing materials, ads, and other brand content to make sure everything stays on track and consistent, no matter where your brand is featured.
Step 7: Measure, Adapt, and Evolve
The key to long-term success is measuring, adapting, and evolving your global brand strategy. Start by using analytics tools to track how your brand performs in different markets, focusing on metrics like brand awareness, engagement, and sales.
Collect feedback from local consumers and teams to get insights into how your brand is perceived and where there might be room for improvement.
Be ready to tweak your strategy based on this data and feedback—global branding isn’t a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Stay flexible and open to changes to keep your brand evolving and resonating in every market.
By following these steps, you can build a strong global brand that resonates with consumers across different cultures and markets.
5 Examples of Global Branding
Here are five examples of successful global branding and how these companies achieved their international success:
1. Coca-Cola

Coca-Cola has found the perfect sweet spot between global consistency and local relevance. Their iconic red and white logo and contour bottles are recognized by almost everyone, everywhere.
With their emotional branding and universal message of happiness and togetherness are loved by everyone. They have adapted their marketing to fit regional cultures.
In many Asian countries, they added local languages and cultural nuances into their ads. They also created localized products, like unique flavours or lower-sugar options, to better suit regional preferences, all while keeping their core brand identity intact.
Coca-Cola’s unique global marketing strategy makes it easier for consumers from all walks of life to resonate with it.
2. Apple

Apple truly knows how to keep things consistent across the globe. No matter if you’re buying an iPhone in the U.S., India or Japan, you’re guaranteed the same sleek design and intuitive interface, all wrapped up in top-notch packaging.
Their global marketing campaigns, like the “Shot on iPhone” series, are designed to resonate everywhere, often highlighting creative expression and innovation.
They also localize these campaigns by featuring images and videos from different countries, making sure the product feels relevant no matter where you are.
And let’s not forget, that Apple’s brand is all about innovation, simplicity, and premium quality—traits they consistently showcase, ensuring their brand stands out globally.
3. McDonald’s

McDonald’s has mastered the art of adapting to local tastes while keeping its core brand identity intact.
Take India, for instance—here you’ll find unique menu items like the McAloo Tikki and Maharaja Mac, which cater specifically to local tastes and vegetarian preferences.
Despite these regional tweaks, McDonald’s keeps its brand consistent with recognizable elements like the Golden Arches, uniform packaging, and a familiar store design across the globe.
They also boost their local relevance by teaming up with local events, sports teams, and celebrities, making sure their brand feels right at home no matter where you are.
4. Nike

Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign is a prime example of how a global marketing strategy can hit the mark across different cultures. The slogan’s simplicity and motivational tone make it easy to translate and impactful no matter where it’s seen.
Nike also knows how to localize their approach by featuring popular local athletes and influencers in their campaigns, like in China, where they team up with well-known sports figures to connect with the local audience.
Plus, Nike lets customers in various regions customize their products online, adding a personal touch while staying true to their global brand identity.
5. Netflix

Netflix has nailed the art of global branding with its See What’s Next campaign, which taps into the universal love for great entertainment. The campaign’s focus on showcasing diverse content speaks to audiences everywhere and celebrates the idea that there’s always something new and exciting to discover.
While the core message stays the same, Netflix smartly tailors its content and marketing strategies to fit regional tastes and preferences. For example, in India, they highlight popular local films and series, making sure the platform feels relevant and connected to viewers’ cultural interests.
Plus, Netflix ensures a consistent user experience across all markets, from seamless streaming to a wide selection of content, so no matter where you are, you know you’re getting top-notch entertainment.
All these companies have successfully built global brands by balancing consistency with local adaptation, ensuring their brand resonates with consumers worldwide while maintaining a strong and recognizable identity.
Final Words
Global branding is more than just expanding your business globally. It’s about creating an identity that resonates across cultures while adapting to the unique needs of local markets. The ultimate goal is to create a brand that transcends borders, stands for something universally valued, and remains flexible enough to thrive in diverse cultural landscapes.
With our expertise, we’ll help your brand grow globally while staying grounded in the local markets you serve. Let us be your partner in crafting compelling content that drives engagement and boosts your global presence.