Keyword Research For SEO: The Complete Guide
Published on November 20, 2024, by Anisha Patel

Google uses 200+ metrics to rank websites. And without a doubt keyword research is the most important step. If you’re struggling to rank your website and attract organic traffic, you should focus on keyword research.
Keyword research will help you identify the right words and phrases to target and improve your content’s performance.
At Provocn, we’ve used proven keyword strategies to help clients improve their search rankings, and this complete guide will show you how to do the same.
- What Is Keyword Research?
- Why Is Keyword Research Important?
- Elements Of Keyword Research
- How To Do Keyword Research?
- Step 1: Define Your Goals
- Step 2: Brainstorm Seed Keywords
- Step 3: Use Keyword Research Tools
- Step 4: Analyse Competitor Keywords
- Step 5: Analyse Keyword Metrics
- Step 6: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
- Step 7: Consider User Intent
- Step 8: Prioritise Keywords
- Step 9: Create Content Around Keywords
- Step 10: Monitor Performance and Refine
- Final Words
What Is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the process of finding, analyzing and using the words and phrases that people use when searching for information, products, or services online.
It is the first step of content creation and is of prime importance. Without good keyword research it’s very hard to rank on the first page of Google.
It gives you an idea of what your target audience is looking for which you can use to create content.
If you can optimize your websites around right keywords it will significantly improve your website’s visibility and drive more and more qualified leads.
Types of Keyword:

1. Short-Tail Keywords (Head Keywords): Short-tail keywords are broad search terms typically consisting of one to three words. They attract high search volume and are commonly used by people who are just beginning their research. However, because they are so general, they are highly competitive, making it difficult to rank for them and convert visitors into customers.
2. Long-Tail Keywords: Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that generally contain more than three words. These keywords cater to users with a clearer intent, such as making a purchase or finding detailed information. Although they have lower search volume, they are less competitive and often result in higher conversion rates due to their targeted nature.
3. Branded Keywords: Branded keywords include the name of a specific company, product, or service. They are used by customers who are already familiar with the brand. These keywords are usually less competitive and more likely to result in conversions because the users searching for them have an existing preference for the brand.
4. Non-Branded Keywords: Non-branded keywords are more generic terms that do not include a specific brand name. They are used to reach a broader audience and are typically searched by users who are still exploring options or gathering information. These keywords are more competitive, but they offer the potential for wider audience reach.
5. LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) Keywords: LSI keywords are terms related to the main keyword that help search engines understand the context of a webpage. These synonyms or closely related phrases improve the relevance of content and enhance SEO performance. Using LSI keywords can help pages rank for a broader set of related queries, improving their visibility and reach.
6. Transactional Keywords: Transactional keywords are used by individuals who are ready to make a purchase or take some other specific action, such as downloading an e-book or signing up for a service. These keywords are highly valuable because they indicate user intent to convert, making them crucial for driving sales or other desired outcomes.
7. Informational Keywords: Informational keywords are searched by users looking for answers, explanations, or educational content. These users are in the research phase, seeking guidance or learning more about a particular topic. While informational keywords can generate high traffic, they are less likely to lead directly to conversions but can build brand awareness and trust.
8. Navigational Keywords: Navigational keywords are used by individuals who are searching for a specific website or webpage. These queries often include brand names or URLs. Users who search for navigational keywords are typically already familiar with the website they’re looking for and are trying to navigate directly to it.
9. Local Keywords: Local keywords are terms that target a specific geographic location. These are essential for businesses that rely on local customers, as they help optimise content for regional search queries. Local keywords are highly effective for local SEO and can drive relevant traffic, especially for service-based businesses or stores.
10. Seasonal Keywords: Seasonal keywords are time-sensitive terms that see a surge in search volume during particular seasons or events. These keywords are perfect for marketing campaigns tied to holidays, special events, or seasonal trends. By optimizing for seasonal keywords, businesses can capture high demand during peak times, but the traffic may drop once the season passes.
Why Is Keyword Research Important?
Keyword research is crucial for several reasons, especially in SEO and content marketing. Here’s why it’s important:
1. Improves Search Engine Rankings: Keyword research helps in identify the terms and phrases that your target audience is searching for. By optimizing your content around these keywords, you increase your chances of ranking higher on search engines like Google.
2. Increases Organic Traffic: When you use relevant, high-volume keywords, you drive more organic traffic to your site. This means more visitors are likely to land on your pages because your content matches their search intent.
3. Ensures Content Relevance: Keyword research helps you understand what your audience is interested in and what problems they’re trying to solve. This allows you to create content that directly addresses their needs, ensuring that your content is relevant and valuable.
4. Competitive Advantage: By researching the keywords your competitors are targeting, you can uncover gaps in their strategy or identify opportunities to outrank them. This gives you a competitive edge in capturing traffic and customers.
5. Better User Intent Alignment: Keyword research reveals not only what people are searching for but also the intent behind their searches (informational, transactional, navigational, etc.). This enables you to create content that aligns with what users are truly looking for, improving conversion rates.
6. Optimizes Paid Advertising: For paid campaigns like Google Ads, keyword research ensures you’re bidding on the right keywords that will deliver the best ROI. By targeting relevant, high-converting keywords, you can optimize your ad spend.
7. Enhances Content Strategy: Keyword research helps you identify long-tail keywords and specific topics to target, allowing you to diversify your content and expand your reach. It also helps uncover content ideas that resonate with your audience.
8. Increases Conversion Potential: Keywords that reflect the customer journey (buy, best, or reviews) can help you attract visitors who are further down the funnel and more likely to convert, leading to higher sales or lead generation.
Elements Of Keyword Research
Here are the core elements of keyword research:
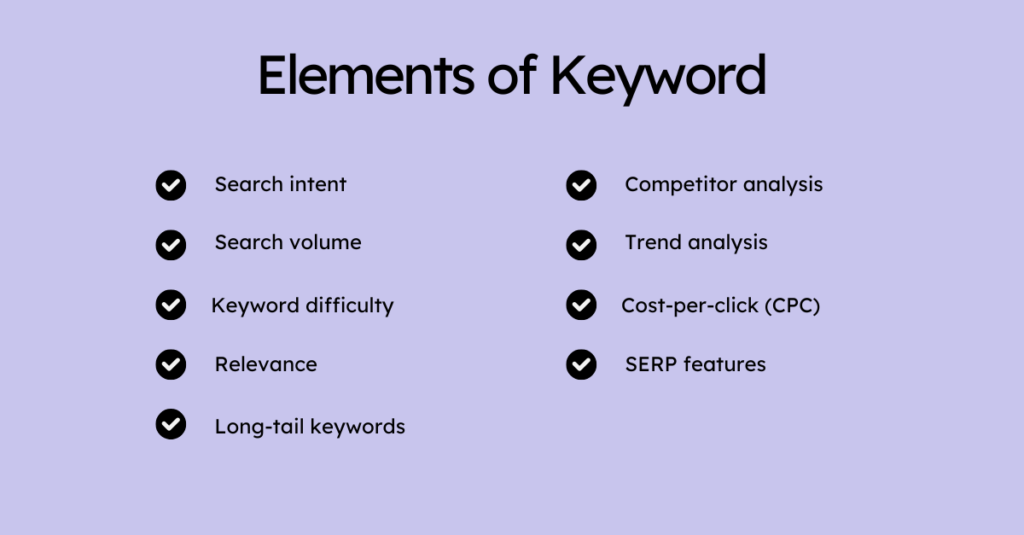
1. Search Intent: It tells why a user is searching for a keyword (e.g., informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial). Example:
- Informational: “How to choose a moisturiser”
- Transactional: “Buy organic moisturiser online”
2. Search Volume: It tells about the number of searches for a keyword in a specific time frame (typically monthly). Prioritise high-volume keywords to attract more visitors while balancing competition.
3. Keyword Difficulty (KD): It tells how hard it is to rank for a keyword based on competition and domain authority.
4. Relevance: It tells how well the keyword aligns with your content, products or services. Avoid targeting high-volume keywords that don’t match your audience or offerings.
5. Long-Tail Keywords: Longer, more specific phrases with lower search volume but higher conversion potential. Instead of targeting “moisturiser”, target “best organic moisturiser for dry skin.”
6. Competitor Analysis: Identifying keywords your competitors rank for and assessing their performance. It helps in finding gaps and opportunities.
7. Trend Analysis: Analyzing seasonal and emerging trends in keyword usage.
8. Cost-Per-Click (CPC): The price advertisers pay for a keyword in PPC campaigns. Indicates the commercial value of a keyword.
9. SERP Features: Examining search engine results pages (SERPs) to understand how a keyword appears (featured snippets, videos, images).
How To Do Keyword Research?
- Step 1: Define your goals
- Step 2: Brainstorm seed keywords
- Step 3: Use keyword research tools
- Step 4: Analyse competitor keywords
- Step 5: Analyse keyword metrics
- Step 6: Focus on long-tail keywords
- Step 7: Consider user intent
- Step 8: Prioritise keywords
- Step 9: Create content around keywords
- Step 10: Monitor performance and refine
Here’s a detailed step-by-step process for effective keyword research:
Step 1: Define Your Goals
Keyword research is the first step of content creation. And defining clear goals is the first step of keyword research. So take a pen and paper or your writing tool and write what you want.
Some examples of goals are:
- Identify search intent
- Improve organic traffic
- Competitor analysis
- Optimise PPC campaigns
- Improve user experience
Next we’ll brainstorm some seed keywords.
Step 2: Brainstorm Seed Keywords
Brainstorming seed keywords is an important step in building a strong foundation for SEO.
- Identify broad terms that are relevant to your industry or your niche.
- Consider what your target audience may type in search bar when looking for your products or services.
- Include related terms, synonyms, and variations of the main keywords.
This will help you create a comprehensive list of keywords that contains the diverse ways users may find your content and products/services.
Step 3: Use Keyword Research Tools
For the third step we’ll use keyword research tools. These tools will help you expand your keyword list and gain insights that you are unaware of.
You can use both free and paid tools for here. A small list of such tools ar:
Free tools:
- Google keyword planner
- Google trends
- Answer the public
- UberSuggest
Paid tools:
- Ahref
- Semrush
- Moz pro
- KWFinder
Here’s how I do my keyword research:
At first I explore Google Autocomplete and the related searches at the bottom of the page, as these can offer further keyword suggestions based on real user searches.
Then I use Google Keyword Planner and entering your seed keywords to generate ideas and view average monthly searches.
For more detailed data, I use SEMrush to get information on keyword difficulty, search volume, and cost-per-click (CPC).
At last I use Answer The Public is useful for generating question-based queries, which helps in finding long-tail keywords.
Step 4: Analyse Competitor Keywords
It’s important to analyse competitor keywords to improve your SEO. Start this process by examining your competitors’ websites to see which keywords they are ranking for.
You can use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush can provide insights into the specific keywords your competitors are targeting, allowing you to assess their approach.
This analysis can help you identify gaps or opportunities where you can target keywords they may have overlooked, giving you a competitive edge in the search rankings.
Step 5: Analyse Keyword Metrics
Analyzing keyword metrics is crucial to understand the potential impact of each keyword. Start by checking the search volume to see how many people search for a specific keyword each month.
Here is a list of things you should check:
- Search Volume: It shows how many people search for a specific keyword each month.
- Keyword Difficulty (KD): It show competitive it is to rank for a keyword.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): It shows the percentage of people who click on a link after seeing it.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC): It indicates how valuable a keyword is for paid campaigns.
Step 6: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Focusing on long-tail keyword is a strategy used to improve SEO performance. It is easier to rank for tonger, more specific phrases. And they often leads to higher conversion rates.
Long-tail keywords address user’s specific needs and highly relevant to searchers intent. They are targeted to a small group of people and have low competition.
By using long-tail keywords in your SEO you can reach a more engaged audience and increase the chances of conversion.
Step 7: Consider User Intent
Let’s focus on intent now. Not everyone who is searching about you wants to buy from you right now. And to know what the want we need to know their intent.
- Informational keywords targets users seeking knowledge. Such as,“how to” or “what is.”
- Transactional keywords targets users with purchase intent. Such as, like “buy XYZ online.”
- Navigational keywords help users find a specific website or brand, such as “Content marketing services.”
- Commercial keywords cater to users who are comparing options before making a decision, for example, “Best content marketing agency”
By aligning your keywords with user intent, you can create content that fulfills the needs of customers at different stages of their journey.
Step 8: Prioritise Keywords
In this step you need to prioritise keywords and find those that’s will work best for you. To prioritise keywords focus on these factors:
- The keywords are highly relevant to your business.
- The keywords attract the right audience.
- Keywords with sufficient search volume (but avoid those with excessive competition that could make ranking difficult).
- Low to medium difficulty (as these are more achievable and can deliver measurable results in the short term).
By prioritising based on these criteria, you can create an effective and targeted keyword strategy.
Step 9: Create Content Around Keywords
Now use the keywords you found and create content around it. Use keywords naturally within the titles, headers, and throughout the content to maintain readability and relevance.
The best places to put keywords are:
- Title
- URL
- Meta
- Headlines
- Throughout the content naturally (No keyword stuffing)
You can also try to create content clusters where a pillar page focuses on broad, high-level keywords and supporting blog posts target long-tail keywords.
This practice will help you cover everything in your niche. From broad topics to specific ones. In long run it will improve your website’s authority and search rankings.
Step 10: Monitor Performance and Refine
Don’t forget to monitor the performance of keywords. You can use tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or keyword tracking features in Ahrefs or Semrush.
If certain keywords aren’t driving traffic or conversions, adjust your content and SEO strategy. This may involve tweaking your content to better align with user intent or making other optimizations to improve performance.
Regularly improving your process based on data ensures your keyword strategy remains effective and responsive to changing search trends.
Final Words
Follow this step by step process when you create content next time.
It will help you find the right keywords which you can use and make your website rank on first page.
Also, remember that content marketing is an ongoing process. So, monitor your performance, refine your strategy and stay adaptable to evolving trends.
And if you need someone to do it for you, you can contact us.
At Provocn, we’ve seen firsthand how powerful keyword research can be in driving business growth. We can do the same for you.